Install Docker Desktop on Mac
Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
Docker Desktop for Mac is the Community version of Docker for Mac. You can download Docker Desktop for Mac from Docker Hub.
By downloading Docker Desktop, you agree to the terms of the Docker Software End User License Agreement and the Docker Data Processing Agreement.
What to know before you install
Relationship to Docker Machine: Installing Docker Desktop on Mac does not affect machines you created with Docker Machine. You have the option to copy containers and images from your local default machine (if one exists) to the Docker Desktop HyperKit VM. When
you are running Docker Desktop, you do not need Docker Machine nodes running locally (or anywhere else). With Docker Desktop, you have a new, native
virtualization system running (HyperKit) which takes the place of the
VirtualBox system.
System requirements
Your Mac must meet the following requirements to successfully install Docker Desktop:
-
Mac hardware must be a 2010 or a newer model with an Intel processor, with Intel’s hardware support for memory management unit (MMU) virtualization, including Extended Page Tables (EPT) and Unrestricted Mode. You can check to see if your machine has this support by running the following command in a terminal:
sysctl kern.hv_supportIf your Mac supports the Hypervisor framework, the command prints
kern.hv_support: 1. -
macOS must be version 10.14 or newer. That is, Mojave, Catalina, or Big Sur. We recommend upgrading to the latest version of macOS.
If you experience any issues after upgrading your macOS to version 10.15, you must install the latest version of Docker Desktop to be compatible with this version of macOS.
Note: Docker supports Docker Desktop on the most recent versions of macOS. Docker Desktop currently supports macOS Mojave, macOS Catalina, and macOS Big Sur.
As new major versions of macOS are made generally available, Docker stops supporting the oldest version and support the newest version of macOS.
-
At least 4 GB of RAM.
-
VirtualBox prior to version 4.3.30 must not be installed as it is not compatible with Docker Desktop.
What’s included in the installer
The Docker Desktop installation includes Docker Engine, Docker CLI client, Docker Compose, Notary, Kubernetes, and Credential Helper.
Install and run Docker Desktop on Mac
-
Double-click
Docker.dmgto open the installer, then drag the Docker icon to the Applications folder.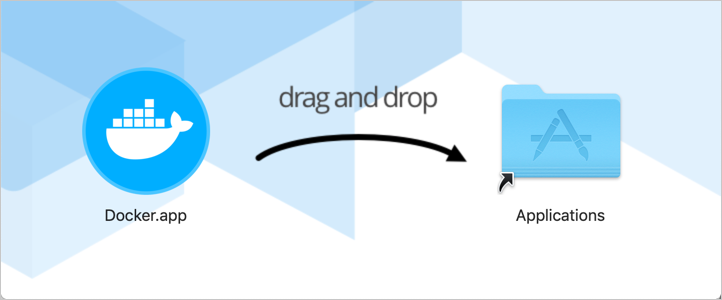
-
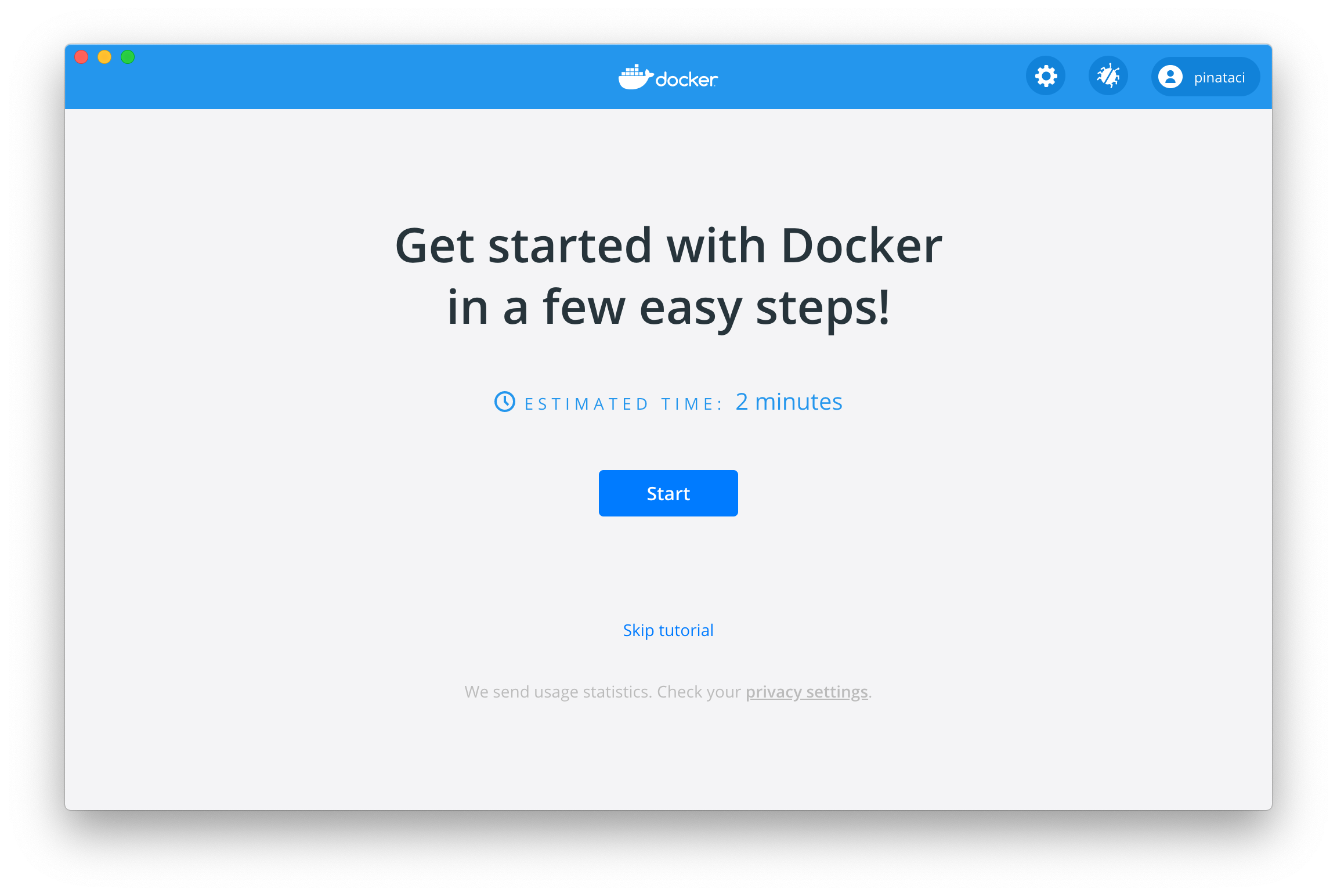
Double-click
Docker.appin the Applications folder to start Docker. (In the example below, the Applications folder is in “grid” view mode.)
The Docker menu in the top status bar indicates that Docker Desktop is running, and accessible from a terminal.

If you’ve just installed the app, Docker Desktop launches the onboarding tutorial. The tutorial includes a simple exercise to build an example Docker image, run it as a container, push and save the image to Docker Hub.
-
Click the Docker menu (
 ) to see
Preferences and other options.
) to see
Preferences and other options. -
Select About Docker to verify that you have the latest version.
Congratulations! You are now successfully running Docker Desktop.
If you would like to rerun the tutorial, go to the Docker Desktop menu and select Learn.
Automatic updates
Starting with Docker Desktop 3.0.0, updates to Docker Desktop will be available automatically as delta updates from the previous version.
When an update is available, Docker Desktop automatically downloads it to your machine and displays an icon to indicate the availability of a newer version. All you need to do now is to click Update and restart from the Docker menu. This installs the latest update and restarts Docker Desktop for the changes to take effect.
Uninstall Docker Desktop
To unistall Docker Desktop from your Mac:
- From the Docker menu, select Troubleshoot and then select Uninstall.
- Click Uninstall to confirm your selection.
Note: Uninstalling Docker Desktop will destroy Docker containers and images local to the machine and remove the files generated by the application.
Save and restore data
You can use the following procedure to save and restore images and container data. For example to reset your VM disk:
-
Use
docker save -o images.tar image1 [image2 ...]to save any images you want to keep. See save in the Docker Engine command line reference. -
Use
docker export -o myContainner1.tar container1to export containers you want to keep. See export in the Docker Engine command line reference. -
Uninstall the current version of Docker Desktop and install a different version (Stable or Edge), or reset your VM disk.
-
Use
docker load -i images.tarto reload previously saved images. See load in the Docker Engine. -
Use
docker import -i myContainer1.tarto create a filesystem image corresponding to the previously exported containers. See import in the Docker Engine.
For information on how to back up and restore data volumes, see Backup, restore, or migrate data volumes.
Where to go next
- Getting started provides an overview of Docker Desktop on Mac, basic Docker command examples, how to get help or give feedback, and links to other topics about Docker Desktop on Mac.
- Troubleshooting describes common problems, workarounds, how to run and submit diagnostics, and submit issues.
- FAQs provide answers to frequently asked questions.
- Release notes lists component updates, new features, and improvements associated with Docker Desktop releases.
- Get started with Docker provides a general Docker tutorial.